- ... equation1
- Like
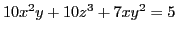
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... states/configurations2
- Logical level, not
physical level
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... 1s.3
- That is
what a state means.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
intuition4
- In Physics, we don't know whether a machine has finite or
infinite states. Though in implementation, a machine seems to have only
finite states, but the fact that such a model even cannot ``count'' is
ridiculous. So we reject the assumption not because the physical fact, but
our intuition.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... sense5
- this means, at any
time, the machine doesn't know about ``all'' the information on the tape,
but only the grid under its ``head''
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... be6
- Wenting has asked a question about how
is Computational System defined, and the answer seems to be: by our intuition...
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... Machine7
- Since Turing
Machines can be encoded into binary strings, Turing Machines are
enumerable.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... input.8
- Inputs are also enumerable, but not
nessesarily so.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... program.9
- This does
not rely on the theorem 2.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... computable.10
- This relies on the theorem 2.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...#tex2html_wrap_inline1734#�11
- Read as ``
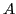 is reducible to
is reducible to 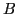 ''
''
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...#tex2html_wrap_inline1744#�12
- This definition is confusing. In the textbook we learned,
the definition of reduction is introduced by defining Oracle first. Of course, we don't have any code for an Oracle.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...#tex2html_wrap_inline1840#�13
- depends
on the specification of this Turing Machine.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...#tex2html_wrap_inline1846#�14
- Used to extend or shrink the tape by managing spaces on the
right end of the tape
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...#tex2html_wrap_inline2006#�15
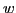 is a computation history for
is a computation history for 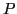 and
and 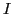 that
shows that
that
shows that 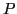 halts.
halts.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...#tex2html_wrap_inline2109#�16
- That is,
for any assignment
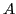 ,
, 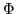 is true.
is true.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ....17
-
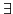 cuicuit such that ...
cuicuit such that ...
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ....18
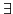 matching
matching
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ....19
-
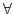 A, A doesn't make F true.
A, A doesn't make F true.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.