Test Case Generator
It would be
nearly impossible to verify every possible combination of inputs but, we would
still like to cover a wide range. We are
able to achieve this by making use of random number generators. Within COELib you will see two types generators,
rand64 and randv. Randv has two
parameterized inputs, SEED and WIDTH.
SEED determines the pseudo-random sequence that will be produced by the
generator. WIDTH is simply the size of
the std_logic_vector output. Place an
instance of randv for both the shamt and ALUop outputs. SEED and WIDTH can then be set by
right-clicking on the component and selecting Object Properites. From here, navigate to the Generic tab, and
initialize the values accordingly. These
components require that SEED is a negative integer. Also, use SEED values that are different from
those shown in figure 5.
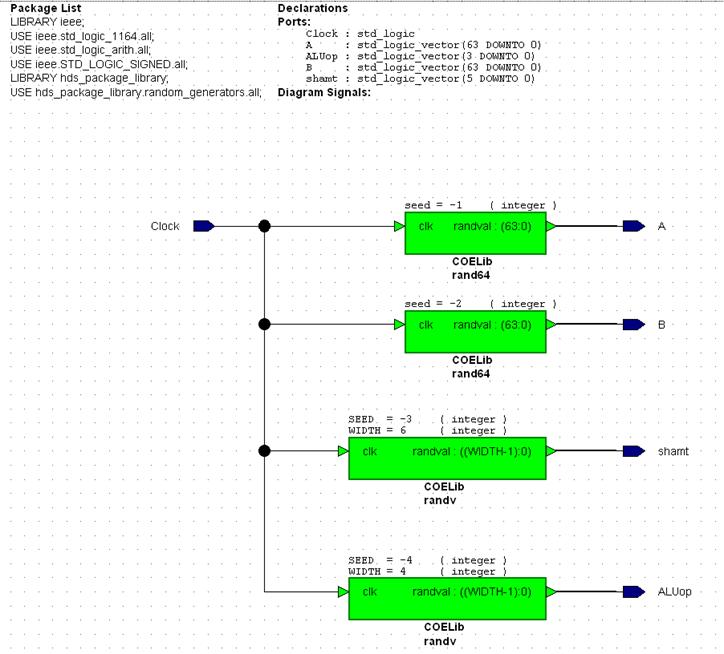
Figure 5
Generating 64
bit inputs (A and B) is a special case, thus you must use the rand64 component
to generate their values. Why are we not
able to just simply use randv and set WIDTH = 64? This will not work because the INTEGER data
type in VHDL does not support integers larger than 32 bits. So that we can fully test our ALU, this
problem was solved by concatenating the outputs of two 32-bit generators that
are seeded differently. Look at the VHDL
for rand64 to see the implementation for yourself.
Click
here to proceed
