Recitation 1
Introduction:
Unlike most recitations, this first recitation will be more like a CS 401 lab. You will be writing a program that uses many of the concepts discussed in CS/COE 401.
Right Triangle Class
Design and program a RightTriangle class (name the class RightTriangle) that represents the triangle's three sides, its area, and its perimeter. Consider what information should be fields and what information should be calculated from those fields. At a minimum, you must store the two legs of the triangle as fields. Below are the methods that your class must provide:
setLegA - Set the length for leg A. This must be a number greater than 0.setLegB - Set the length for leg B. This must be a number greater than 0.getLegA - Get the length for leg A.getLegB - Get the length for leg B.- Set and get methods for any other fields you choose to store. Be sure to validate any values passed into the mutator methods.
getHypotenuse - Get the hypotenuse of the triangle.getPerimeter - Get the perimeter of the triangle.
Your mutator methods must handle the case that they are given bad values. They should not assign the bad value to the field. They must alert the user (i.e. the programmer using your RightTriangle class) that the value was bad.
The class must maintain encapsulation and data abstraction.
Name your class RightTriangle.
Demonstrate that your class behaves as described by writing a program in a separate file. The program must have the following steps:
- Set the length of leg A to 5.
- Set the length of leg B to 10.
- Set any other fields to appropriate values (if necessary).
- Call
getHypotenuse and print out the returned value.
- Call
getPerimeter and print out the returned value.
Conceptual Questions:
Consider the following questions:
- If you chose to store any fields (other than leg A and leg B), justify your reason for choosing them to store. If you chose to only store leg A and leg B, explain why you did not choose any other fields to store.
Final Notes
A right triangle is a triangle where one angle is a right angle (i.e. 90 degrees). The side of the triangle opposite that right angle is called the hypotenuse; the other two sides are called legs. An image of a right triangle is shown below.
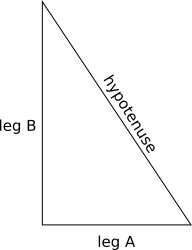
The formula for calculating the hypotenuse is: SQRT(A2 + B2), where A is the length of leg A, B is the length of side B, and SQRT is the square root function (which you can find in the Math class).
The formula for calculating the triangle's perimeter is: A + B + hypotenuse, where A is the length of leg A, B is the length of side B, and hypotenuse is the length of the hypotenuse.
Submission and Grading:
This is for your practice. You should be able to complete this before the end of recitation. If you do, call the TA over to look over your program to make sure it is correct. If you do not have time to complete it before the end of recitation, you have the option of uploading it to CourseWeb once you are finished to receive feedback on it from the TA. If you upload it after Monday, September 7, please email the TA so he knows to look at it.
