

Quantitative Fault Models
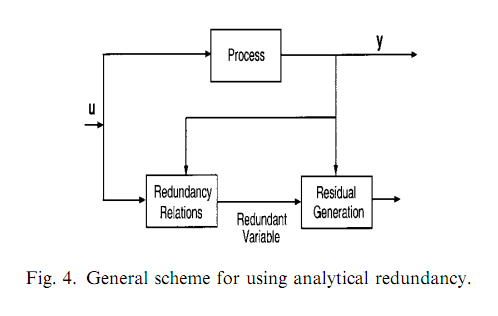
Analytical redundancy - Takes advantage of mathematical relationships between process variables to provide redundancy checks
Residual generation in dynamic systems - y(t) = f(u(t), w(t), x(t), Omega(t)) where y(t), u(t) are measureable outputs and inputs, x(t) and w(t) are the state variables and disturbance within the system, Omega is process parameters. From y(t) and u(t), x(t) or Omega(t) can be estimated.
Hardware redundancy and voting schemes - Replicated hardware used to detect fault by disagreement
Img source: Venkatasubramanian et al


