![]() Knowledge Systems Institute
Knowledge Systems Institute
![]() BA513 Multi-media Information Systems
BA513 Multi-media Information Systems
Wireless bank and WML
Prof : Dr. S.K Chang
Student : Jin Lung Chen
How does a WAP device connect to the internet?
The normal implementation of a WAP scenario looks pretty much like this:
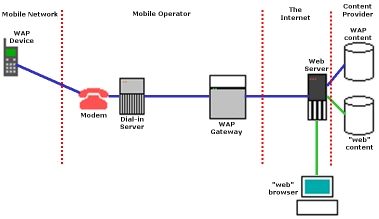
In the figure above, starting from the left,
you'll find the mobile WAP device attached to the mobile network (GSM, CDDA, etc) which
dials the modem attached to a dial-in server (RAS, or Remote Access Service). This server
gives the WAP device access to the protocols it needs. These are the same lower level
protocols as a normal Internet Service Provider will give you. This is known as PPP or
Point-to-Point Protocol.
These protocols are used to access the next step in the chain, the WAP gateway, in this
figure hosted by the mobile operator. The WAP gateway is the link between the wireless and
the "web" world, basically giving the WAP device access to the common internet.
(1) Wireless application
IntegrationWireless develops applications that support WAP/WML, the standard for wireless
data access. This means that anyone with a WAP-phone or handheld computer with wireless
data access can use our applications. The devices support by the applications, which
run on phones from Nokia, Ericsson, Motorola, and almost any other wireless device.
(2) WAP gateway
A WAP gateway is a piece of software that has several
functions in the "chain" between the WAP device and the web server. These
functions are in general:
*Converting the markup language (WML) from textual format to tokenized
(binary/compressed) format which is readable by the WAP device.
*Translating the requests from the WAP device to HTTP requests for the "web"
world.
*Convert between the SSL encryption used in the "web" world and the WTLS
encryption used in the WAP world.
*Convert between the "transport" protocol of the "web", TCP, and that
of the WAP world, WDP.
The reason for the conversion from texual WML to tokenized WML is to reduce bandwidth
usage. A WAP device's WML browser can only read tokenized WML.
(3) Web sever
On the internet, there is a normal "web" server which in this case holds both WAP and "web" contents, which now receives the request to send out the contents located at the http://wap.colorline.no/ URL. Also note the normal "web" browser at the lower part of the figure. The web server, depending on which type of browser it is talking to (WAP or "web"), sends out WAP, represented by the blue line, or "web" content represented by the green line.
(4) URL
The URL, the WML browser, when receiving the tokenized WML code renders the contents on the WAP device's display to present a card for the user.
¡@
¡@