CS 2310 Projectí¬ Just-in-Time Medical Application
IC System
Design
I.
IC System for Initialization
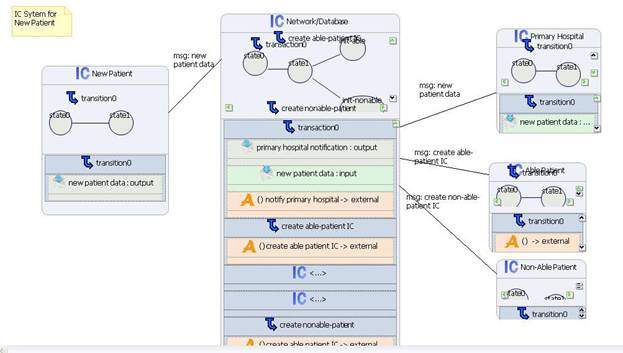
1.1 New Patient Initialization
n
A new
patient will provide data about himself/herself
n
This
data will be stored in the networkí»s database.
n
The
hospital that the patient has selected as his/her primary hospital will be
notified of its new patient.
n
The
new patientí»s data will indicate that the user is either capable of taking care
of himself or not.
q
If the
patient cannot take care of himself, a new non-able patient index cell is
created by the system.
q
Otherwise,
a new able patient index cell is created by the system.
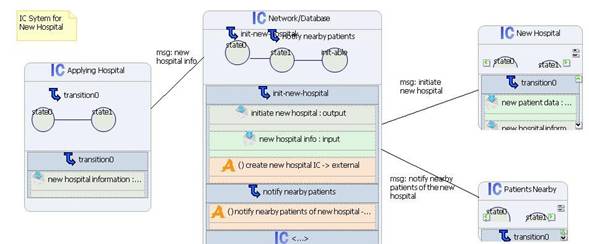
1.2 New Hospital Initialization
n A new hospital will provide information
about itself to be stored on the network.
n A new Hospital index cell is created
n Based on the location of the hospital,
nearby patients will be notified in order to provide them the opportunity to
change their primary hospital (this would be a separate scenario for changing
primary hospital).
1.3 New Expert Initialization
n A new expert will provide his/her
credentials to the network, as well as the hospital at which he/she works.
n
A new
Expert index cell is created
n
Patients
who may be interested in such a specialist will be notified so that they may
switch their primary hospital.

II.
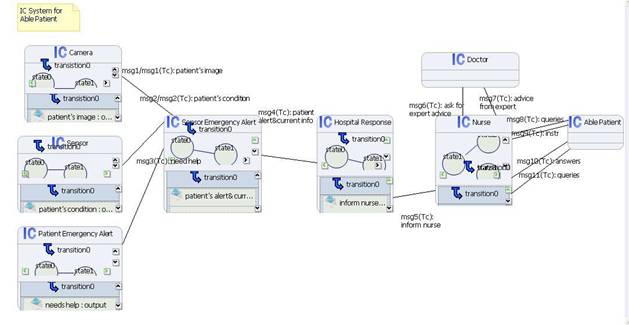
IC System for Able Patient
n
In
this able-patient scenario, an able patient can make alert request by
himself/herself.
n
Sensor
Emergency Alert cell
receives messages from both the patient (Patient Emergency Alert) and
the Sensor and/or Camera, and it forwards the information to Hospital
Response cell.
n
Then Nurse
is informed and the nurse can interact with the Able Patient, making
queries and instructing the patient
n
The
patient follows the nurseí»s instructions, answers questions and makes queries.
n
If the
nurse is not sure about what to do, she can ask for advice from the Doctor.
(the same as í░Expertí▒)
III.
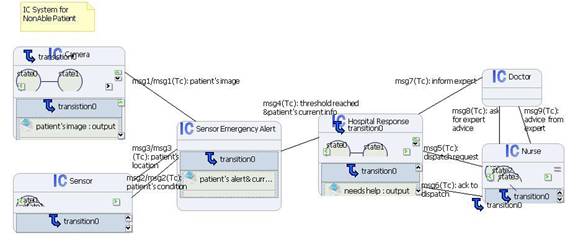
IC System for Non-Able Patient
n
In
this non-able patient scenario, a non-able patient cannot make alert request by
himself/herself, so alert is initiated by Sensor and/or Camera.
n
Sensor
Emergency Alert cell
forwards the alert information to Hospital Response cell when some
parameter threshold is reached.
n
Both
the Doctor and Nurse will be informed.
n
Nurse
will be dispatched to assist the non-able patient if necessary. When a nurse
receives the dispatch task request, he/she should make acknowledgement.
n
Nurse
and doctor will be informed of the current conditions of the non-able patient
sent by sensor and camera, and nurse can communicate with doctor.
IV.
Timing Constraints on Messages
n
In all
of the time-critical messages, Tc is the time parameter. Once such a
message arrives at the target IC, a checking for the time will be done.
n
Let
current system clock be Ts.
n
If Ts
< Tc then the IC is not triggered.
n
If
Tc+Tnormal >= Ts >= Tc then the output message will carry a new time
parameter Tc'(Tcí» = Tc+Tnormal.).
n
If
Tc+Talarm >= Ts > Tc+Tnormal, i.e., Tc is within an alarm threshold
Talarm, then an alarm message is sent to request immediate response.
n
For different
ICs, the Tnormal and Talarm can be different, so that we can flexibly set
reasonable thresholds to best meet our application.
Specifically, the
timing constraints in the messages for the above three IC Systems:
n
For
the initializations, messages are not time-critical, so they do not carry any
time parameters.
n
For
the able patient IC system, almost all messages are time-critical, because this
is a just-in-time application meaning requests should be resolved within
limited timing budget. A special case is msg1 and msg2 as depicted in the
figure: Before alert is detected, the sensor and/or camera just periodically
send messages which have no time parameters (here I just simply put down msg1: patientí»s image and msg2: patientí»s condition). However, once
ití»s known that an alert exists in the network, the messages msg1 and msg2 are
time-critical, because they have to be delivered in time to ensure effective
interactions between nurse& patient(or between doctor& nurse). Thus
msg1 and msg2 should carry time parameters, in the form of msg1 (Tc): patientí»s image and msg2
(Tc): patientí»s condition.
n
For
the non-able patient IC system, the timing constraints work in the same way as
the able-patient scenario.