Tree structures
Each node is associated with a temporal operator and each leaf represents a basic object. The set of temporal operators depends on the system.
CMIF:
Proposes both sequential and parallel operators.
SRT:
Has sequential and equal operators.
equal operators - the operands start simultaneously and must have the same duration.
static checking phase is used to verify that the operands of an equal operator have the same duration.
SRT is not able to deal with unpredictable events.
SMIL:
Have more advanced set of operators to express interruptions like Par_min.
Authoring Capabilities:
It is not straightforward to get the tree structure from the scenario.
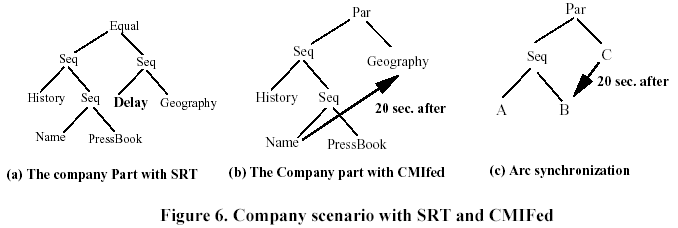
Figure 6(a) illustrates the Company part of the document example, using SRT. The only way to get a tree structure is to fix the delay between the beginning of History and Geography. Notice that the temporal information between Geography and Name is lost.
Synchronization Arcs in CMIF:
Allows additional temporal information between any pair of nodes of the tree.
Figure 6(b), shows a Synchronization Arc from Name to Geography specifying a delay of 20 s.
Semantics of Synchronization Arcs is unclear. Figure 6(c), What happens if the A is longer than 20 s?