Conclusions
The work is summarized in the table of Figure 12 where a comparison of the different systems according to the different issues (1 to 15) is done. The fifteen issues, identified throughout this work, are recalled below:
|
|
A wide variety of basic objects and a rich set of operations on them (issue 1) |
|
|
The possibility to control the delivery of continuous objects (issue 2) |
|
|
Interactivity capabilities attached to objects (issue 3) |
|
|
Temporal style definitions (issue 4) |
|
|
A support for unpredictable objects (issue 5) |
|
|
Temporal Composition (issue 6) |
|
|
Interactions (issue 7) |
|
|
Adaptability to computer illiterate people (issue 8) |
|
|
Straightforward design (issue 9) |
|
|
Indeterministic scenario authoring capabilities (issue 10) |
|
|
Ease of local modifications (issue 11) |
|
|
Fast editing/presentation cycle (issue 12) |
|
|
Abstraction capabilities (issue 13) |
|
|
Multimedia document models (issue 14) |
|
|
Multigrids reading support (issue 15) |
We use a three levels notation for that table:"-" the issue is not addressed, "+" the issue is a major concern of the system and "+/-" the issue is partially supported. When we have no information, we use a "?".
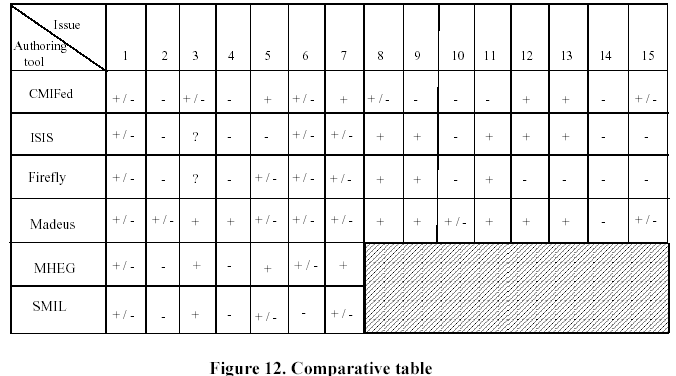
We can draw the following main remarks from this table:
|
|
Each system/language partially fits the first issue but none of them is able to provide fine temporal operations on objects: no distinction between mapping (respectively unmapping) and starting (respectively stopping) of objects and no pause and resume actions. |
|
|
Temporal style definition issue (issue 4) has not been fairly taken care of, although it is an essential feature to build attractive multimedia documents (see for example the numerous programmed animations on the Web). |
|
|
It is difficult to compare the temporal composition feature (issue 6) of the studied systems because this issue is clearly related to the inputs and the outputs taken into account by the system (see issues 1 to 5). As we have stated in 2.2, even if Allen's relations can be expressed by all of them, they are not equivalent when considering their ability to control the delivery of continuous objects. |
|
|
Except in CMIFed, the interaction issue (7) is weakly addressed, mainly because local interactions raise difficulties in a constraint-based context. |
|
|
Constraint-based approaches are better adapted for satisfying author needs (issues 9 and 11) thanks to the relative approach they allow. |
|
|
Document modeling has not yet been considered for multimedia documents (issue 14) but it is clear that it will become a main issue when such documents become widely used. |