

Structure:
The Key to the composite pattern is an abstract
class that represents both primitive elements (concepts, text, and
graphics) and their containers (subtopics). Following figure shows the
general structure of the composite pattern:
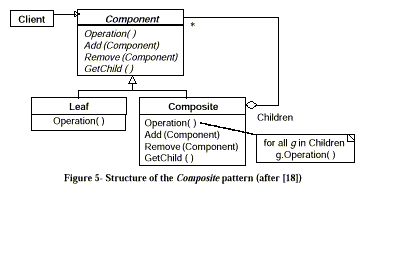
Participants and Collaborations:
The abstract class in the
figure is responsible for providing a common interface to all objects in
the composition, both simple (conceps, text, and graphics) and complex
(topics and subtopics). The add and remove functions are examples of
functions from such a common interface. It also defines the interface for
accessing the child components of a complex object (a topic or a
subtopic), e.g. the functions Operations and Getchild. The concrete
classes Leaf (corresponding to simple contents of a lesson in the
example) and composite (corresponding to topics and subtopics) are derived
from component. The Leaf class represents leaf objects in the composition
and has no children.



